Understanding heat shrink ratios is crucial to choosing the proper tubing for your project. This guide will explain heat shrink ratios, how they work, and how to select the right one for your needs.
What Is a Heat Shrink Ratio?
A heat shrink ratio refers to the relationship between the heat shrink tubing’s original size (diameter) before heat is applied and its final size after shrinking. It is typically expressed as a ratio, such as 2:1, 3:1, or 4:1, indicating how much the tubing will shrink in size.
For example:
2:1 ratio
The tubing will shrink to half (50%) of its original diameter.
3:1 ratio
The tubing will shrink to one-third (33%) of its original diameter.
4:1 ratio
The tubing will shrink to one-fourth (25%) of its original diameter.
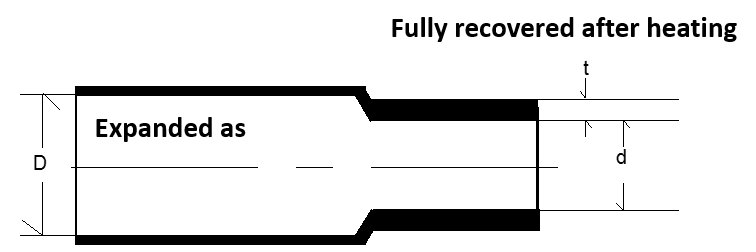
The first number in the ratio represents the original size, and the second number represents the final size after heat is applied. Higher ratios indicate greater shrinkage, allowing the tubing to fit over larger components and shrink tightly for a secure fit.
How Does Heat Shrink Tubing Work?
Heat shrink tubing is made from polymer materials, such as polyolefin, that expand during manufacturing and “remember” their smaller, original shape. When heat is applied (typically using a heat gun), the tubing contracts to its predetermined size.
This shrinking process happens evenly along the tubing’s length, ensuring a uniform and secure fit around the objects it covers. Depending on the tubing’s material, the shrinking temperature typically ranges from 90°C to 250°C.
Common Heat Shrink Ratios
The most commonly used heat shrink ratios are 2:1, 3:1, and 4:1. Each has specific advantages depending on the application:
2:1 Heat Shrink Ratio
This is the most common ratio used in general applications. A 2:1 ratio means the tubing shrinks to half its original size. It works well for standard wire insulation, cable bundling, and component protection.
- Use Case: Ideal for situations where the diameter of the component is not significantly larger than the cable or wire being covered.
- Example: If you start with a 10mm diameter tube, it will shrink to 5mm once heated.
3:1 Heat Shrink Ratio
A 3:1 ratio allows the tubing to shrink to one-third of its original size. This makes it suitable for covering irregularly shaped or larger components and offers more versatility in fitting over connectors, joints, or splices.
- Use Case: Great for applications requiring more significant shrinking, such as sealing larger cables or irregularly shaped objects.
- Example: A 15mm diameter tube will shrink to 5mm after heating.
4:1 Heat Shrink Ratio
This ratio offers the highest level of shrinkage, reducing the tubing to one-fourth of its original size. It is perfect for covering extremely large or irregular shapes and is often used in outdoor or harsh environments where robust insulation is required.
- Use Case: Typically used in extreme environments, such as marine, aerospace, military, or heavy-duty industrial applications where strong environmental protection is critical.
- Example: A 20mm diameter tube will shrink to 5mm after applying heat.
Choosing the Right Heat Shrink Ratio
Selecting the appropriate heat shrink ratio depends on the specific needs of your project. Consider the following factors:
Size of the Object:
Measure the largest diameter of the object that needs to be covered. Then, choose heat shrink tubing with a diameter large enough to fit over the object before shrinking.
Final Fit:
Ensure the tubing will shrink enough to provide a tight fit. A higher ratio, like 3:1 or 4:1, may be necessary if the object is small or irregularly shaped.
Environmental Conditions:
If the tubing is exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or physical abrasion, choose a material with the right level of protection and the correct shrink ratio.
Application Type:
For standard wiring and electrical insulation, a 2:1 ratio is usually sufficient. A 3:1 or 4:1 ratio provides better coverage and durability for larger cables, connectors, or harsh environments.
Heat Shrink Material Considerations
While the shrink ratio is essential, it’s also important to consider the type of material used in the tubing. Common materials include:
Polyolefin:
The most popular material for general use, offering flexibility, flame resistance, and protection against chemicals.
PVC:
It is known for being cost-effective and flame retardant, but it has a lower shrink temperature than polyolefin.
Heat shrink tubing is invaluable for insulation, protection, and cable management across industries. Understanding heat shrink ratios allows you to select the appropriate tubing for your specific application. A 2:1 ratio is great for general use, while a 3:1 or 4:1 ratio offers more versatility for larger or irregular components. Always consider the size of the object and the environment in which it will be used to ensure the best fit and protection.
By matching the proper heat-shrink ratio with the correct material, you can significantly enhance the durability and safety of your electrical and mechanical components.
For all your heat shrink tubing needs, you can contact us at:





